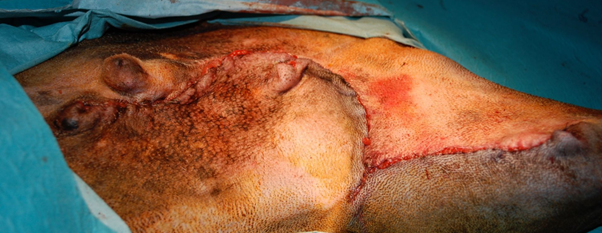
What is an axial vessel?
An axial vessel is a direct cutaneous artery that forms the basis for an axial pattern flap by supplying the subdermal plexus in the skin.
What is a local flap?
Local flaps are flaps that are created using skin adjacent to the defect. There are two kinds of local flap, the axial pattern flap and the random pattern flap.
What is a random pattern flap?
Random pattern flaps are flaps that are based on the subdermal plexus of vessels and capillaries within the skin. The advantage of random flaps over axial pattern flaps is that they can be created anywhere in the body where there is skin laxity. The disadvantage is that they survive to a lesser degree when compared with axial pattern flaps.
What is a regional pattern flap?
Regional flaps are flaps that are made in the same general area where the defect is. The donor site is connected to the recipient site by a bridging incision.
What is a distant pattern flap?
There are two different types of distant pattern flap:
- Pedicled flaps are connected by a strip of skin at the base of the flap where the donor site and recipient site are far apart and there is intact skin in between. The pedicle may be formed into a tube outside the skin.
- Free flaps are like axial pattern flaps but the feeding vessels are transected and reimplanted on a donor vessel in the recipient site.
What is an island flap?
An island flap is the kind of flap that is not connected to the donor site by skin. Instead, it is connected via the direct cutaneous artery, which is tunnelled under the skin between the donor site and the defect to be closed.
What is a peninsular flap?
A peninsular flap is the same thing as a single pedicle flap which may or may not be based on a direct cutaneous artery.
What is a transposition flap?
Transposition flaps (a.k.a. lifting flaps) are a type of flap that uses noncontiguous donor tissue that is incised and lifted over intact skin and placed into the primary defect.
What is a local advancement flap?
A local advancement flap is often a rectangular flap in which three sides of the rectangle are cut, leaving one of the short sides intact. The skin is then stretched to cover a defect adjacent to the non-intact short side of the rectangle.
How is flap surgery done?
Flaps surgery is done in different steps which include:
identifying the defect which is to be closed investigating the reconstructive procedures which would be appropriate for the area elevating the donor skin while maintaining the blood supply if necessary transferring the skin to the recipient site suturing it in place closing the donor site defect.
What’s the difference between a flap and a graft?
A flap is a piece of skin transferred from the donor site to the recipient site with the blood supply intact. A graft is a piece of skin transferred without its blood supply intact and is reliant on the formation of a new blood supply at the recipient site.
What is rotational flap surgery?
Rotation flaps are a type of flap that provides the ability to mobilize large areas of tissue with a wide vascular base for reconstruction. The name rotation flap refers to the vector of motion of the flap, which is curved or rotational. The procedure involving these flaps can be thought of as the closure of a triangular defect by rotating the adjacent skin around a rotation point (or fulcrum) into the defect.
What is Z plasty surgery?
A Z-plasty is a tension-relieving technique wherein a “Z” incision is made with the central portion aligned with the line of tension. The flaps of skin are reoriented into an “N” shape thereby increasing the length of the central portion by about 50%. It is a very effective way of reducing linear tension in the skin where there is extra skin oriented in the perpendicular axis.
Does flap surgery hurt?
Because flap surgery is done under either local or general anaesthetic, the procedure itself should not be painful. Following surgery, the degree of pain suffered by the patient is generally moderate and can be mitigated by the use of analgesic medications including opioids, non-steroidal anti inflammatory medications, paracetamol and acetaminophen.
How long does flap surgery take to heal?
Generally, flap surgery takes about 2 weeks to heal. However, the healing process can be affected by:
blood supply Infection movement at the surgery site the age and nutritional status of the patient some medications
What is flap failure?
Flap failure occurs when the skin fails to heal in place at the recipient site. This can be caused by: inadequate blood supply infection excessive tension seroma formation excessive movement during recovery